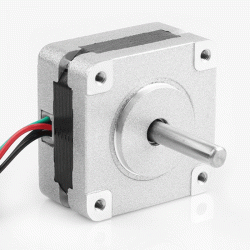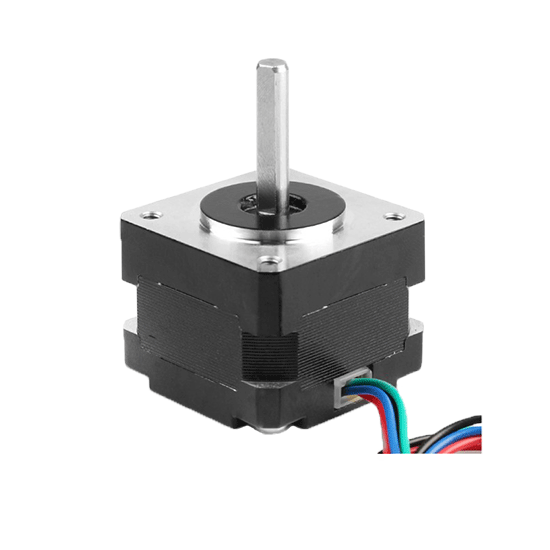
- Stock: In Stock
- Model: P-35BYGH220-236
- SKU: P-35BYGH220-236
Available Options
- Step Angle Accuracy: ±5% (full step.no load)
- Resistance Accuracy: ±10%
- Inductance Accuracy: ±20%
- Temnerature Rise: 80℃ Max. (rated current, 2 phase on)
- Ambient Temperature: -10℃~+50℃
- Insulation Resistance: 100MΩ Min.500VDC
- Dielectric Strength: 500VAC·5mA for one Min.
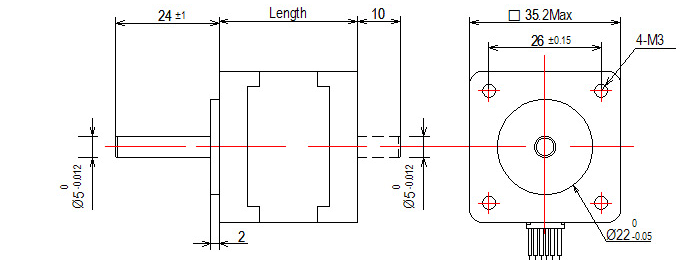
- Shaft Radial Play: 0.06Max. (450 g-load)
- Shaft Axial Play: 0.08Max. (450 g-load)
- Insulation Class: Class B 130°
- Warranty: 12 months
- Certificate: CE, ROHs, ISO/SGS9001
| Model | Rated Voltage | Rated Current | Phase Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | Motor Leads | Rotor Inertia | Weight | Length | ||
| Single Shaft | Double Shaft | ||||||||||
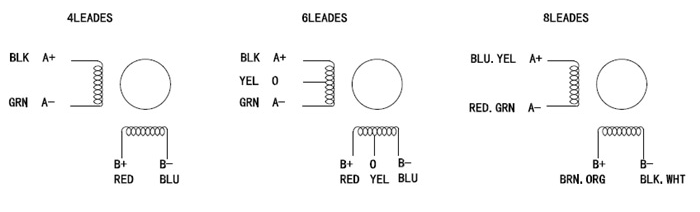
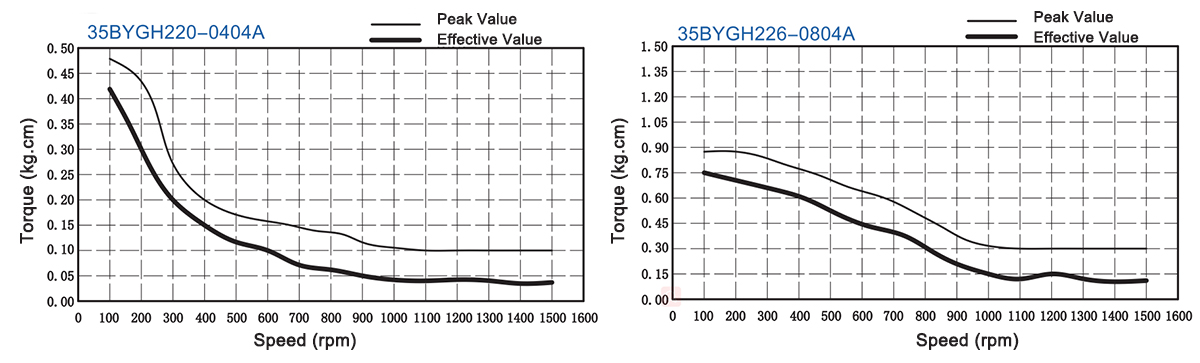
| P-35BYGH220-0404A | P-35BYGH220-0404B | 10V | 0.4A | 25Ω | 8mH | 7oz-in | 0.5kg-cm | 4 | 8g-cm2 | 0.1kg | 20mm |
| P-35BYGH226-0804A | P-35BYGH226-0804B | 3.8V | 0.8A | 4.8Ω | 10mH | 11oz-in | 0.8kg-cm | 4 | 10g-cm2 | 0.12kg | 26mm |
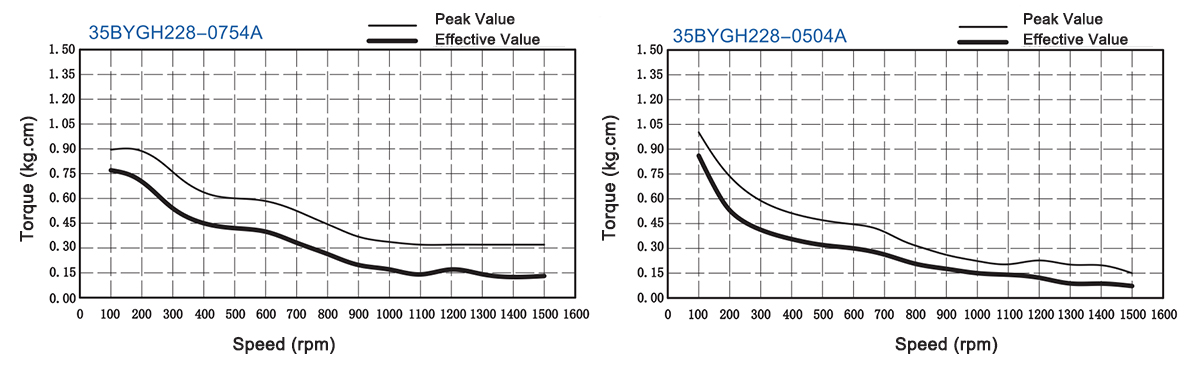
| P-35BYGH228-0754A | P-35BYGH228-0754B | 3.2V | 0.75A | 4.3Ω | 10mH | 11oz-in | 0.8kg-cm | 4 | 10g-cm2 | 0.14kg | 28mm |
| P-35BYGH228-0504A | P-35BYGH228-0504B | 10V | 0.5A | 20Ω | 10mH | 14oz-in | 1.0kg-cm | 4 | 10g-cm2 | 0.14kg | 28mm |
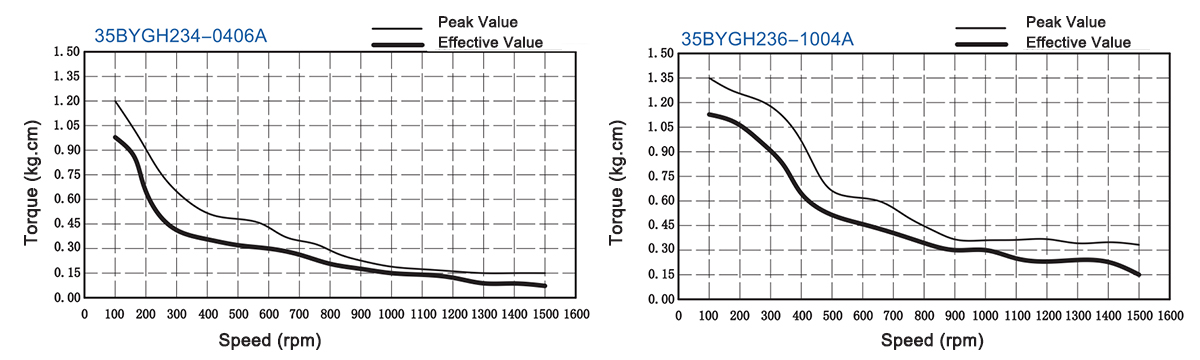
| P-35BYGH234-0406A | P-35BYGH234-0406B | 10V | 0.4A | 25Ω | 14mH | 17oz-in | 1.2kg-cm | 6 | 14g-cm2 | 0.17kg | 34mm |
| P-35BYGH236-1004A | P-35BYGH236-1004B | 2.7V | 1A | 2.7Ω | 14mH | 19oz-in | 1.4kg-cm | 4 | 14g-cm2 | 0.18kg | 36mm |
NEMA 14 Stepper Motor Wiring Diagram
Stepper motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy based on the principle of electromagnetics. People began to use this kind of motor as early as the 1920s. As the embedded systems (such as 3D printers, disk drives, toys, wipers, vibrating pagers, robotic arms and video recorders, etc.) is increasingly popular, more and more people use stepper motors.
Stepping motors not only are used in industry, military, medical, automotive, but also are applied in entertainment. Stepper motors play a very import role in moving an object from one position to another. Thus, a stepper motor is definitely needed in handy.
Stepper motors have many shapes and sizes. Generally speaking, they can be classified into two categories, which are variable reluctance stepper motors and permanent magnet stepper motors. The stepping motor is driven by a set of coil windings on the stator cogging, the fixed part of the motor. Usually, a wire wound in a loop is called a solenoid. However, the wire wound around a tooth is called a winding, coil or phase in a motor.