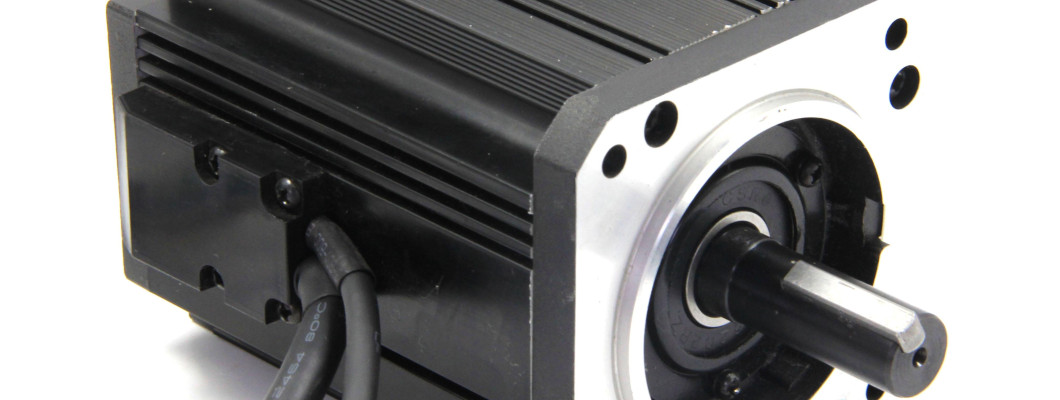

Brushed Motor
When the brushed motor is working, the coil and the commutator rotate, but the magnetic steel and the carbon brush do not rotate. The alternating change of the current direction of the coil is accomplished by the commutator and brush that rotates with the motor. In the electric vehicle industry, brushed motors include high-speed brushed motors and low-speed brushed motors. There are many differences between brushed motors and brushless motors. Judging from the name, it can be seen that brushed motors have carbon brushes, while brushless motors do not have carbon brushes.
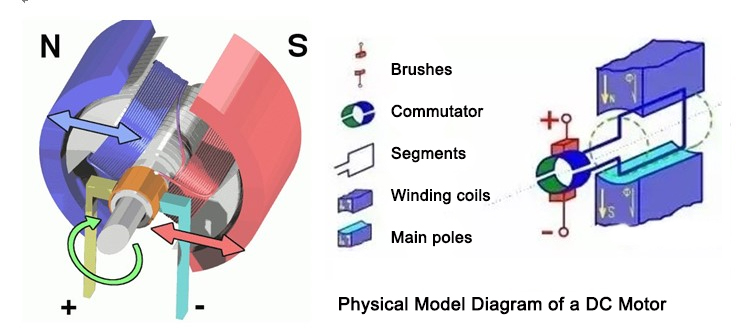
The brushed motor consists of two parts: stator and rotor. The stator has magnetic poles (winding type or permanent magnet type) and the rotor has windings. After being electrified, a magnetic field (magnetic pole) is also formed on the rotor. There is an angle between the magnetic poles of the stator and the rotor, which makes the motor rotate under the mutual attraction of both stator and rotor magnetic fields (between the N pole and the S pole). The position of the brush varies from the direction of the angle between the stator and rotor poles to change the direction of rotation of the motor.
Brushless Motor
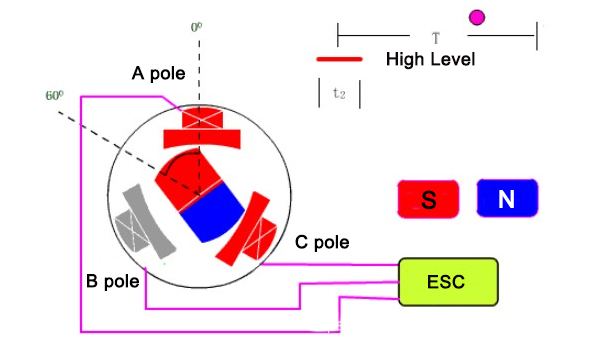
The brushless motor adopts electronic commutation, its coil does not move and the magnetic pole rotates. The brushless motor adopts a set of electronic equipment to sense the position of the magnetic pole of the permanent magnet through the Hall element. According to such a perception, the electronic circuit is used to switch the direction of the current in the coil timely to ensure that the magnetic force in the correct direction is generated to drive the motor, which eliminates the disadvantages of brushed motors.
These circuits are the brushless motor controllers. The brushless motor speed controller can also realize some functions that the brushed motor cannot, such as adjusting the power switching angle, braking the motor, making the motor reverse, locking the motor, and stopping the power supply to the motor by using the brake signal. Nowadays, the electronic alarm lock of the battery car makes full use of these functions.
The brushless DC motor consists of a motor and a brushless motor driver, which is a typical mechatronic product. Since the brushless DC motor is operated by automatic control, it will not add another starting winding on the rotor like a synchronous motor with heavy load under variable frequency speed regulation and will not produce oscillation and loss of step when the load changes suddenly.
Brushless Motor vs Brushed Motor
- Difference in Speed Regulation
Both the brushless motor and the brushed motor are controlled by regulating voltage. The brushless DC adopts electronic commutation, so its speed regulation can only be realized by digital control. However, the brushed DC is commutated through carbon brushes. It is relatively simple to use traditional analog circuit control such as thyristor.
1. The brushed motor speed regulation process is to adjust the voltage of the motor power supply. The adjusted voltage and current are converted through the commutator and the brush to change the strength of the magnetic field generated by the electrodes to achieve the purpose of changing the rotational speed. This process is called variable speed regulation.
2. The speed regulation process of the brushless motor is that the voltage of the power supply of the motor remains unchanged, the control signal of the ESC is changed, and the switching rate of the high-power MOS tube is changed by the microprocessor to realize the change of the speed. Such a process is called variable frequency speed regulation.
- Performance Difference
1. Brushed motors are traditional products with relatively stable performance. On the contrary, the brushless motor is an upgraded product and its life performance is better than that of the brushed motor. However, its control circuit is more complex and has higher requirements for components.
2. Service life. The brushless motor can work continuously for about 20,000 hours and the conventional service life is 7-10 years. However, the service life of brushless motors also varies for different bearings. While the continuous working life of brushed motors is usually several hundred to more than one thousand hours. When reaching the limit of use, carbon brushes need to be replaced, otherwise it is easy to cause bearing wear.
3. In terms of energy saving, the power consumption of brushless motors is relatively only 1/3 of that of brushed motors. BLDC motors are controlled by frequency conversion technology, which will save more energy than series motors. For example, the frequency conversion air conditioners and refrigerators are the typical applications.
4. Effects in use. Brushless motors are usually controlled by digital frequency conversion, featuring strong controllability and it is possible to achieve a few revolutions per minute or tens of thousands of revolutions per minute easily. On the other hand, the brushed motor generally works at a constant speed after starting and it is not easy to adjust the speed. The series motor can also reach 20,000 rpm, but its service life will be relatively short.
5. Different applications. Brushless motors are usually used in such equipment that require high control and high rotational speed, such as model aircraft, precision instruments, etc. and they can be used in the dairy industry, brewing industry, meat processing industry, soy product processing industry, beverage processing industry, pastry processing industry, pharmaceutical industry, electronic precision factory and other dust-free workshops with higher requirements. But brushed motors are usually adopted in power equipment, such as hair dryers, factory motors, household range hoods, etc., and they can not be used in dust-free workshops and explosion-proof workshops. In addition, the speed of series motors can also reach high, but due to the wear and tear of carbon brushes, their service life is not as good as brushless motors.
6. Routine maintenance. The brushed motor needs to be replaced. If the replacement is not timely, the motor will be damaged. However, the brushless motor has a longer service life, which is more than 10 times longer than that of the brushed motor and the motor needs to be replaced if it is damaged, but the daily maintenance is unnecessary.
| Difference | Brushed Motors | Brushless Motors |
| Structure | Simple | Complex |
| Technology | Mature | Not mature enough |
| Maintenance | Convenient to replace carbon brush | Can only replace the motor |
| Cost | Low | High (With controller) |
| Control | Easy | A little complicated |
| Response speed | Fast | Slow |
| Starting torque | Large (low speed) | Relatively small |
| Variable speed | Gentle | Vibration |
| Braking effect | Smooth, good | Unstable, large vibration |
| Control Precision | High accuracy 0.01 mm | Using a locator pin or limiter |
| Speed Regulation Mode | Variable voltage speed regulation | Frequency control of motor speed |
| Unit mass torque | Small | High |
| Unit power torque | Small | High |
| Reliability | Low | High |
| Heat dissipation | Slow | Fast |
| Interference | Moreover, with an electric spark | Small, sparkless |
| Noise | Much, brush | Low |
| Service life | Short, 5000h | Long, 20000h |
| Energy consumption | Larger | Smaller |
| Failure rate | High | Low |
| Applications | Precision instruments, printers, etc. | Constant speed equipment, air conditioning refrigerator, unmanned aerial vehicle dust-free, explosion-proof, food and other industries. |
